This test evaluates the psychotic like effects of a pharmacological challenge (NMDA receptor antagonist – MK-801) by studying drug-induced hyperlocomotion. This test is applicable to rats and mice.
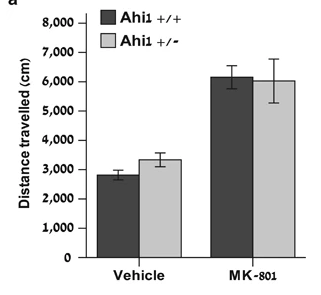
Using an open field arena (50 × 50 × 33 cm under 15 lux illumination), young-adult male C57BL/6 mice, both wildtype and heterozygous Ahi1 knockout (Ahi1+/−), were injected intraperitoneally with MK-801 0.15 mg kg−1 or saline. After 30 min, animals could explore the arena for 6 min while their movements were recorded using Ethovision (Noldus Information Technologies, Wageningen, The Netherlands). Main effect of treatment (vehicle vs MK-801) was significant (F1,45=52.828, P<0.0005), but main effect of genotype and genotype × treatment interaction were nonsignificant. n=12–13 mice per group. (Reproduced from Lotan et al, Molecular Psychiatry, 2014).
References:
van den Buuse M. Modeling the positive symptoms of schizophrenia in genetically modified mice: pharmacology and methodology aspects. Schizophr Bull. 2010.
Lotan A, Lifschytz T, Slonimsky A, Broner EC, Greenbaum L, Abedat S, Fellig Y, Cohen H, Lory O, Goelman G, Lerer B. Neural mechanisms underlying stress resilience in Ahi1 knockout mice: relevance to neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Feb;19(2):243-52. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.123. Epub 2013 Sep 17.
