Transient blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) by potent selective antagonists such as dizocilpine (MK-801) during a sensitive early neurodevelopmental window has been show to trigger widespread apoptotic neurodegeneration and oxidative stress in the developing cortex, alongside long-lasting cognitive-behavioral deficits relevant to schizophrenia. Thus, models based on early transient NMDAR blockade have emerged as valid and reliable platforms for gaining pathophysiological insights into early disease-related perturbations
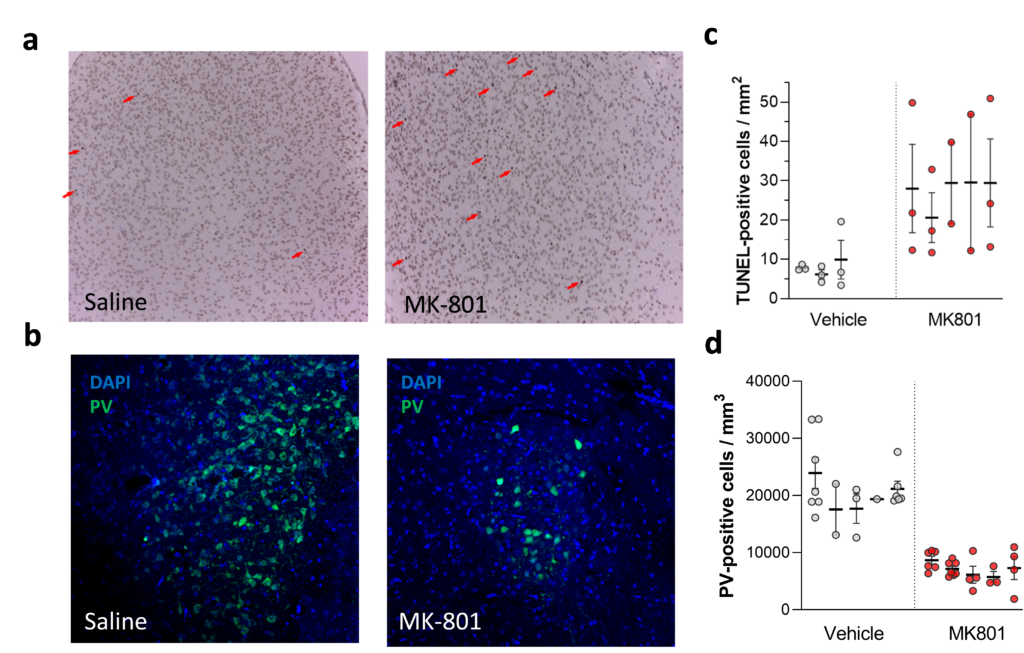
Neonatal C57Bl/6 mice were administered two intraperitoneal injections of saline or MK801 (0.5 mg/kg) on PND 6 and culled on PND 7. (a) TUNEL staining of representative brain specimens. Arrows depict TUNEL-positive cells, reflecting DNA fragmentation and often considered a proxy for apoptotic cells death. (b) Confocal microscopy depicting a sagittal section of a representative PND7 mouse brain stained with fluorescent antibodies for PV, which localize in a subcortical region corresponding to the MGE (white square, magnified for subsequent analysis). (c-d) Quantifications of (c) TUNNEL and (d) PVI. Each column in the scatterplot depicts specimens obtained from an individual mouse, highlighting means ± sem. Significance obtained from independent-samples t-tests. 3-5 mice/group, with 3-7 sections/mouse. Upon reaching adulthood, mice that had been transiently treated with MK801 on PND 6 displayed long-lasting cognitive-behavioral alterations, including impairment of working memory (assessed by alternation index in the Y-maze working memory paradigm) and an anxiety-like phenotype (reflected by thigmotactic behavior in a novel open field arena). Significance values obtained from two-way-ANOVAs controlling for sex. n=11(saline), 25(MK801).
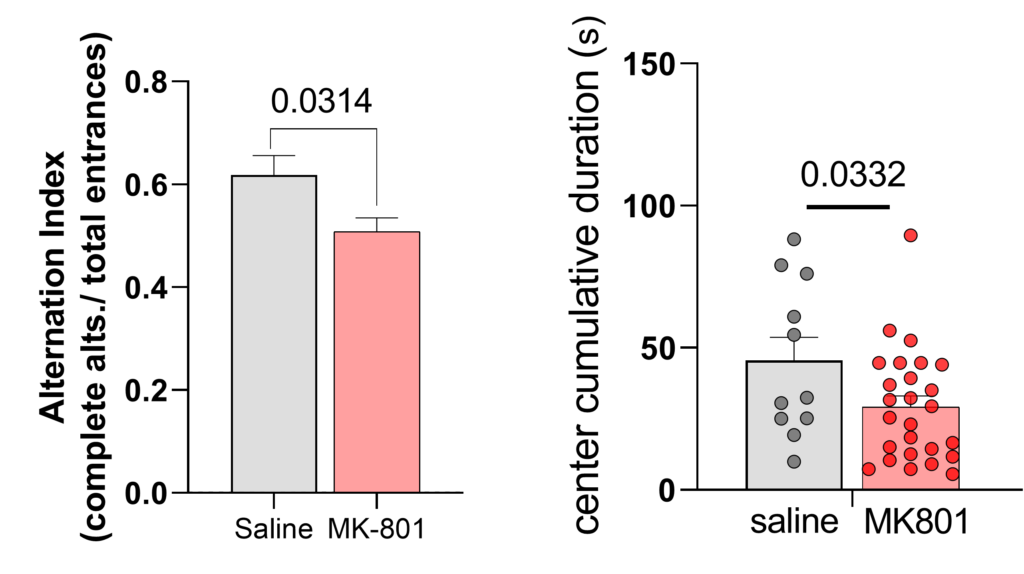
Upon reaching adulthood, mice that had been transiently treated with MK801 on PND 6 displayed long-lasting cognitive-behavioral alterations, including impairment of working memory (assessed by alternation index in the Y-maze working memory paradigm) and an anxiety-like phenotype (reflected by thigmotactic behavior in a novel open field arena). (Unpublished Data, Hadassah BrainLabs).
References:
Stefani MR, Moghaddam B. Transient N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade in early development causes lasting cognitive deficits relevant to schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2005 Feb 15;57(4):433-6.
